Breakthrough in Alpha-Gal Syndrome Treatment: Exploring Auricular Acupuncture
Auricular Acupuncture: A New Hope for Treating Alpha-Gal Syndrome
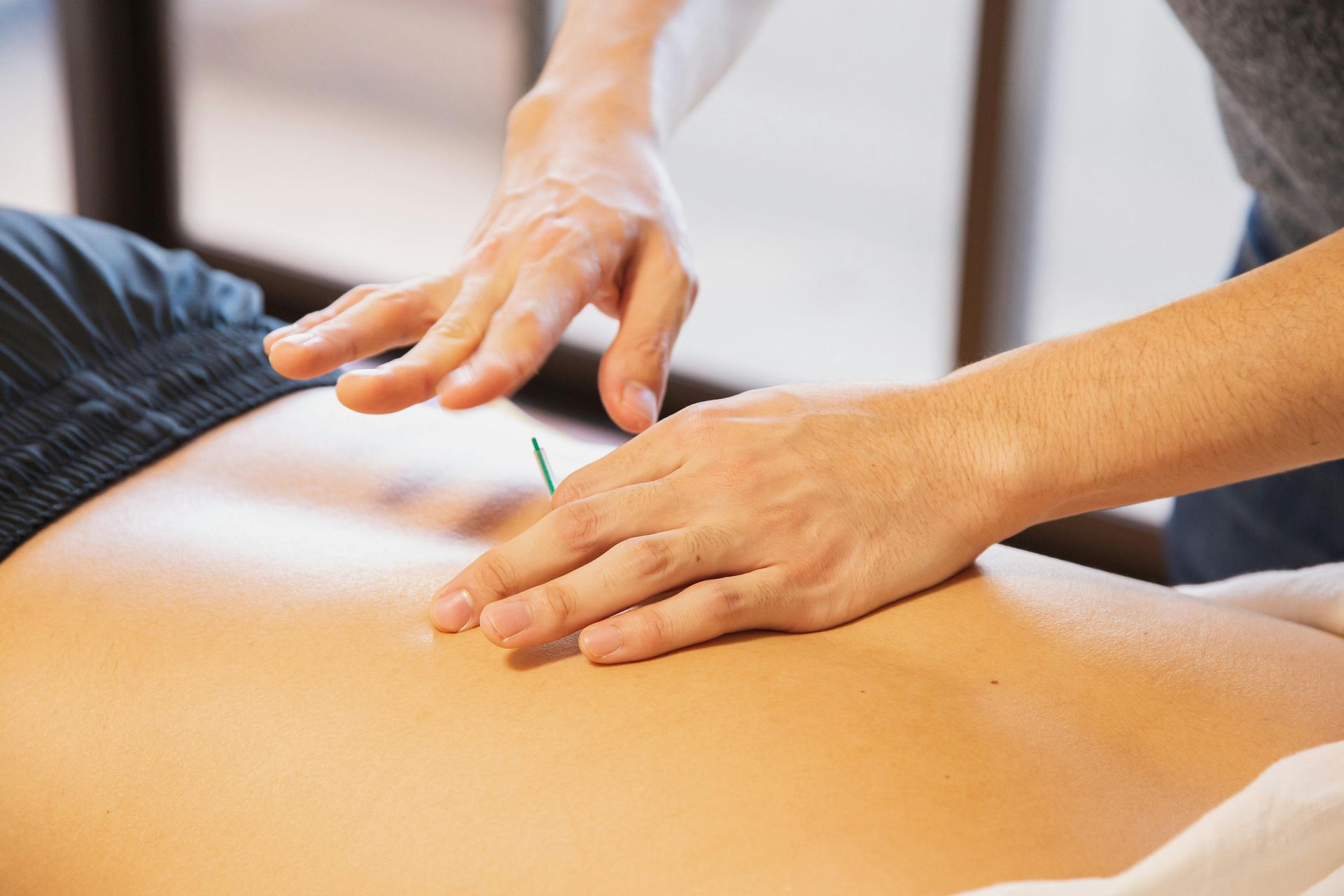
Alpha-gal syndrome (AGS) is an allergic reaction to mammalian meat triggered by the bite of a Lone Star tick, resulting in sensitivities to alpha-galactose, a sugar found in mammalian products. The hallmark symptom of AGS is delayed anaphylaxis, which can occur hours after consuming red meat or other mammal-based products. Unfortunately, the only known way to manage AGS is through strict dietary avoidance, making daily life for patients particularly difficult.
However, a recent case series published in Medical Acupuncture highlights a potentially transformative treatment: auricular acupuncture. Specifically, the Soliman Auricular Allergy Treatment (SAAT) shows promise in addressing the root of AGS. This study tracked 137 patients diagnosed with AGS who underwent SAAT at two clinics in the U.S. Results were astounding: 96% of patients reported complete remission of their symptoms and were able to reintroduce mammalian meat into their diets. These results mark a major step forward in treatment options for a condition that has long been considered untreatable.
Understanding Auricular Acupuncture and SAAT
Auricular acupuncture is a therapeutic modality that involves stimulating points on the outer ear to treat health conditions. The procedure specifically used in this case series, SAAT, involves the insertion of a needle into a designated point on the ear, which remains in place for three weeks. This method is believed to stimulate the body’s immune and nervous systems in ways that help reduce allergic sensitivities.
SAAT has been particularly effective in treating various allergies, and AGS is no exception. The study involved carefully monitoring patients, and post-treatment follow-up ranged from 3 to 60 months to assess long-term effects. Remarkably, patients continued to report symptom resolution well after the needles were removed, indicating that the benefits of SAAT are not just temporary but possibly permanent.
Case Series Findings
The case series involved a diverse range of patients, each with a confirmed diagnosis of AGS based on clinical history and testing. These patients experienced a variety of AGS symptoms, including urticaria, gastrointestinal issues, and anaphylaxis. Their cases were monitored over a period of months and even years to assess the effectiveness and safety of SAAT.
In nearly every case, the treatment was effective. Within weeks of treatment, patients reported being able to consume mammalian products without experiencing adverse effects. Additionally, none of the participants reported severe side effects from the treatment. In fact, those who had previously experienced anaphylactic reactions before the treatment were able to consume meat safely post-treatment.
Implications for Future Research
The results of this study are particularly exciting given the growing number of AGS cases. With climate change and habitat shifts increasing the prevalence of the Lone Star tick, more people are at risk of developing AGS. Traditionally, AGS patients have been left with limited options, and the emotional toll of strict dietary restrictions can be significant. SAAT offers a glimmer of hope, not just for AGS sufferers but for allergy sufferers in general.
While the results of this study are promising, the authors also call for more rigorous, randomized controlled trials to confirm the effectiveness of SAAT on a larger scale. The study's success in providing long-term relief to a majority of patients is a critical step in validating alternative treatments for AGS. It opens up new avenues for exploring how the body's nervous system can be harnessed to reduce allergic sensitivities.
The Path Forward
If future research confirms these findings, auricular acupuncture could revolutionize treatment approaches for AGS and potentially other food allergies. The low-risk, minimally invasive nature of SAAT makes it an attractive option for patients seeking alternatives to conventional methods that rely solely on avoidance strategies. Moreover, as interest in integrative medicine grows, SAAT might see broader applications in clinical practice.
For now, SAAT represents a beacon of hope for those who struggle with the debilitating effects of AGS. Although it requires more exploration to become mainstream, this case series is a major step forward, offering a path toward not only managing but potentially curing the condition.
For more details, you can read the full study here.




